Research
Emphathize
Conduct user research to uncover genuine pain points and user needs that are not met.
Step 01
Plan User Research
Establish overarching research goals and clarify specific outcomes to achieve.
Project Essentials
- Project background and context
- Identify who is affected by the design
- Define deliverables the research should yield
Decide what to conduct
- User Interviews
- Shows contextual relationships between data points and uncovers hidden motivations.
- Fly on the wall
- Observe behaviors in natural environment without interfering or biasing the subject.
- Quantitative Surveys
- Big data collection that provides statistical significance and spread of numbers.
Step 02
Recruit Participants
Recruit a diverse participant pool.
Get a Good Mix
- Develop criteria to select best suited interviewees for your objectives.
- Get 5-8 people per user group/persona you are studying, but reduce this if you have
budget/timeline constraints (this is only the start after all)
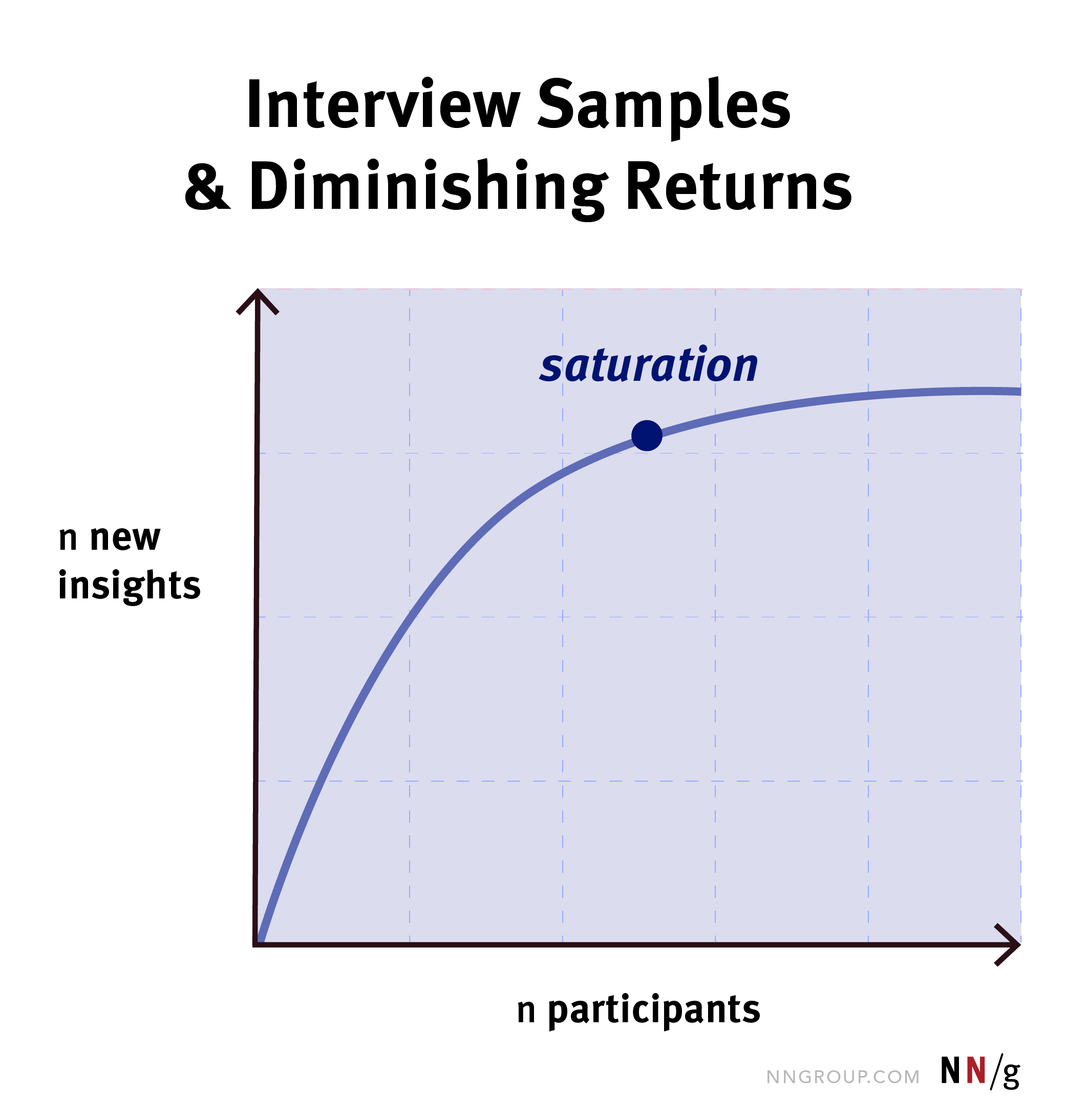
Source: Nielsen Norman Group
Getting Them
- Get people from existing user base, online, hallway testing
- Consider giving incentives
Step 03
Conduct Interviews
Engage directly with users through structured conversations to uncover their genuine motivations and behaviors.
Prepare for interviews
- Script interview questions
- Collect supplies (e.g. laptop, printed questions, markers)
- Email interviewees for 1-1 interviews as far as possible
- Book conducive spaces and travel to their location if it's best
- Remind them of interviews
Interviewing them
- Thank users for coming, gather basic details, ask permission to record
- Speak clearly & concisely, remain professional. Be active listener - nod, make appropriate eye contact, write notes
- Ask open-ended questions, start with “why” questions.
- If given short “yes” or “no” answer, ask neutral follow-up question to get them to share more.
- Take notes, highlight compelling quotes, write down observations about participants, record interviews
- Thank participants once done
Define
Analyze research from empathize phase to identify and prioritize key user problems that need solving, explaining rationale behind these priorities.
Step 01
User Stories
User stories are “checklists” to ensure we address and solve key problems they might face with product.
Write User Stories
- Concisely capture user needs
- Prioritize design goals
- Foster user-centric empathy
- Justify decisions by showcasing user benefits
- Should be succinct yet impactful
- Should have clear action and benefit
- Create one-sentence narratives from a persona’s viewpoint that define who user is, what
they want to accomplish, and why.
Example
As [type of user], I want to [action] so that [benefit].
Step 02
Draw User Journeys
Write user journeys for your users.
Mapping the Path
- Draw sequence of experiences a user undergoes in attempting to achieve their goal.
- Think about user pain points. Are they because of financial, product, process, customer support pains?
- After you define pain points, answer Who, What, When, Where, Why, and How to solve problems.
Step 03
Problem Statement
Formulate clear problem statement and develop value proposition.
Defining the Core Issue
- Summarize who user is, what they need from design, and why
- Ensure design caters to various user types by crafting problem statements for each user
persona, thus aligning product development with diverse user needs.
Example
[Name of user persona] is a [type of user] who needs [type of user experience] because [benefits of user experience].
Ideate
Think of something.
Step 01
Develop Hypotheses
Frame your design challenges as actionable questions and predictions to guide the ideation process.
Hypothesis Frameworks
- Create hypothesis statements on what solution might be.
- Use "How Might We". Good HMW accommodates many solutions, but keep focused on these
solutions.
Example
If [action], then [outcome] - Or use it in a we believe format:
Example
We believe that [action] will [outcome]. - Ensure hypothesis statements establish what user can do/achieve, what desired outcome that we call successful
Step 02
Come Up With Design Solutions
Generate many ideas without judging quality.
Idea Generation
- Transform problem statement into "How might we" questions.
- Rapid sketching: Divide a sheet into squares (8), sketch ideas anything (even crazy stuff), keep to timed intervals.
- Do competitive audits to analyze competitors' products, strengths, & weaknesses.
- Applying SCAMPER method: Substitute, combine, adapt, modify, put to another use, eliminate, & rearrange elements.
Step 03
Assess Feasibility
Ground your creative solutions in reality by evaluating them against technical, business, and timeline constraints.
The Reality Check
- Assess ideas based on feasibility within budget and schedule constraints and alignment with design standards.
- Determine if design idea has value - what does it do and why should users care?
Prototype & Test
Make something.
Step 01
Prototype
Create an initial model of a product that showcases its features and allows for testing.
Evolution of Fidelity
- Develop a sitemap to organize product by defining its hierarchy and sequence, illustrating topics' importance and navigational flow.
- Produce wireframes, both paper-based and digital (using tools like Figma or Adobe XD), to visually represent product's layout and interface.
- Construct low-fidelity prototypes to provide a basic interactive model of product, allowing for initial user interaction feedback.
- Advance to high-fidelity prototypes that closely mimic final product with detailed components and interactivity for thorough testing.
Step 02
Test
Validate your design decisions and uncover usability issues through structured, iterative user testing.
Validation Strategy
- Integrate testing throughout prototyping phase to refine design continuously based on
user feedback:
- Begin with simple sketches or sitemaps to gather initial feedback.
- Progress to more detailed paper prototypes for another testing round.
- Further iterate to a high-fidelity, interactive model for additional user testing.
- Potentially test multiple prototypes or same prototype across different devices to optimize user experience.
- Establish a comprehensive testing plan to refine prototype effectively:
- Determine who will participate in tests, from informal feedback circles to target users.
- Define what types of tests will be conducted, considering both prototype's stage and testing environment.
- Clarify why tests are conducted, primarily to validate earlier design decisions and uncover usability issues.
- Outline how participants will interact with prototype and how information will be collected during tests, ensuring inclusivity and accessibility.